Nutritional Information Overview

Egg mcmuffin no cheese nutrition – Let’s dive into the specifics of the Egg McMuffin’s nutritional profile, focusing on the version without cheese. Understanding the nutritional breakdown helps you make informed choices about your diet. This information is based on McDonald’s official nutritional data, which can vary slightly depending on location and preparation.
The Egg McMuffin without cheese offers a relatively balanced breakfast option, providing a good source of protein and some essential vitamins and minerals. However, it’s important to consider its fat and sodium content within the context of your overall daily intake.
Nutritional Content of an Egg McMuffin (Without Cheese)
The following table details the approximate nutritional content per serving. Remember that these values are averages and may vary slightly.
| Name | Amount | % Daily Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 300 | 15% | kcal |
| Total Fat | 17g | 21% | g |
| Saturated Fat | 6g | 30% | g |
| Cholesterol | 260mg | 87% | mg |
| Sodium | 500mg | 21% | mg |
| Total Carbohydrate | 31g | 10% | g |
| Dietary Fiber | 2g | 8% | g |
| Total Sugars | 3g | – | g |
| Protein | 17g | 34% | g |
| Vitamin D | 2mcg | 10% | mcg |
| Calcium | 10% | 10% | %DV |
| Iron | 8% | 8% | %DV |
| Potassium | 6% | 6% | %DV |
Nutritional Differences Compared to a Standard Egg McMuffin, Egg mcmuffin no cheese nutrition
The primary difference between an Egg McMuffin with and without cheese lies in the addition of cheese. Cheese significantly increases the calorie, fat, and sodium content. The cheese adds saturated fat and cholesterol, impacting the overall nutritional profile. A standard Egg McMuffin typically contains around 300-350 more calories and substantially more fat and sodium than the cheese-less version.
Ingredient Analysis: Egg Mcmuffin No Cheese Nutrition
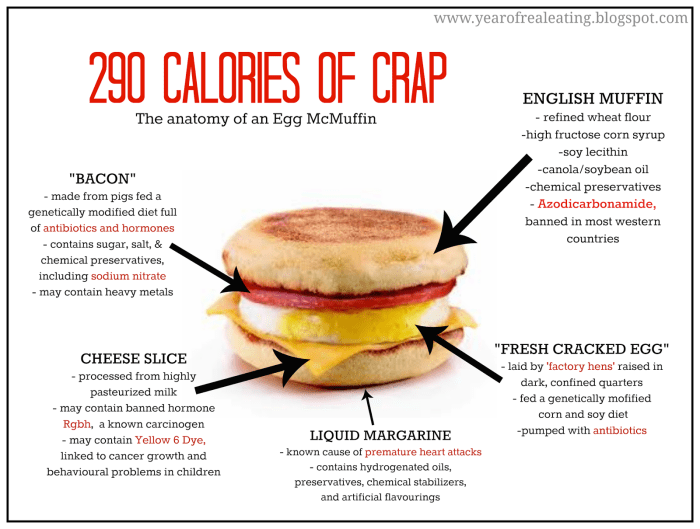
Let’s break down the components of an Egg McMuffin (no cheese) to understand its nutritional profile. We’ll examine each ingredient’s contribution and highlight potential allergens. Understanding this helps make informed dietary choices.
The Egg McMuffin (without cheese) primarily consists of three main components: a fried egg, a Canadian-style bacon slice, and an English muffin. Each contributes unique nutrients and potential allergens.
So, you’re looking at the nutritional breakdown of an Egg McMuffin without cheese? It’s a pretty standard breakfast option, relatively low in fat compared to some other fast food choices. But let’s consider a contrasting example: if you’re curious about the significantly higher calorie and fat content of pastries, check out the cheese danish nutrition facts ; it’s a world apart from the Egg McMuffin.
Then you can really appreciate the lighter side of the Egg McMuffin, no cheese, of course.
Ingredient Nutritional Contributions
The nutritional value of each ingredient varies slightly depending on sourcing and preparation, but here’s a general overview. The egg provides protein, essential fatty acids, and vitamins like choline and vitamin D. The bacon offers protein and some B vitamins, but is also high in saturated fat. The English muffin contributes carbohydrates, some fiber, and a small amount of protein.
The combination creates a relatively balanced meal in terms of macronutrients, though the fat content is notable.
Potential Allergens
Individuals with allergies should exercise caution when consuming an Egg McMuffin. Key allergens to consider include eggs (present in the fried egg), gluten (potentially present in the English muffin, depending on preparation and ingredients), and milk (potentially present as a trace ingredient in the processing of other components, even if not explicitly listed as an ingredient). Always check the ingredient list and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any allergies or sensitivities.
Impact of Processing Methods
The processing methods used in preparing the Egg McMuffin affect its nutritional value. Frying the egg can increase its fat content compared to a poached or boiled egg. The bacon undergoes a curing process that might impact its nutrient profile. The English muffin’s baking process also influences its nutritional characteristics. While convenient, these processing methods can lead to higher levels of saturated fat and sodium compared to a homemade version using fresh ingredients and alternative cooking methods.
Comparison with Other Breakfast Options

Choosing a breakfast sandwich can be tricky! Understanding the nutritional differences between various options helps you make informed decisions about your morning meal. This section compares the Egg McMuffin (no cheese) to other breakfast choices, both within McDonald’s and beyond.
Egg McMuffin (No Cheese) vs. Other McDonald’s Breakfast Sandwiches
The following table compares the nutritional profile of an Egg McMuffin (no cheese) with other popular McDonald’s breakfast sandwiches. Note that nutritional information can vary slightly depending on location and preparation. These values are approximate and should be used as a general guideline.
| Item | Calories | Fat (g) | Protein (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Egg McMuffin (no cheese) | 290 | 13 | 17 |
| Sausage McMuffin (no cheese) | 370 | 23 | 15 |
| Bacon, Egg & Cheese Biscuit | 420 | 23 | 19 |
| Steak, Egg & Cheese Biscuit | 480 | 28 | 24 |
Egg McMuffin (No Cheese) vs. Other Popular Breakfast Foods
The Egg McMuffin (no cheese) provides a good source of protein, but its fat and calorie content is relatively high compared to some other breakfast options.
- Oatmeal: A serving of oatmeal (1/2 cup dry) offers significantly fewer calories and fat, while still providing fiber and some protein. The nutritional profile is highly dependent on added ingredients like sugar or fruit. Plain oatmeal is a healthier choice.
- Yogurt (plain, nonfat): Yogurt is a great source of protein and calcium, with lower fat and calories than the Egg McMuffin (no cheese). Again, added sugars significantly impact the nutritional value.
- Toast (whole wheat): Two slices of whole-wheat toast provide fiber and complex carbohydrates, with relatively few calories and fat. The addition of toppings such as butter or jam will increase the calorie and fat content.
Nutritional Value Per Calorie Comparison
This table shows the relative nutritional value per calorie for each food item, providing a more nuanced comparison beyond simply looking at total values. This is calculated by dividing the amount of each nutrient by the total calories. The values below are approximate.
| Item | Calories | Fat (g/100 calories) | Protein (g/100 calories) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Egg McMuffin (no cheese) | 290 | 4.5 | 5.9 |
| Sausage McMuffin (no cheese) | 370 | 6.2 | 4.1 |
| Oatmeal (1/2 cup dry) | 150 | 2.0 | 3.3 |
| Yogurt (plain, nonfat, 1 cup) | 150 | 0.0 | 10.0 |
| Whole Wheat Toast (2 slices) | 150 | 1.3 | 4.0 |
FAQ Overview
Is the Egg McMuffin (no cheese) a good source of protein?
Yes, it provides a decent amount of protein, making it a suitable option for those looking to incorporate protein into their breakfast.
Does the Egg McMuffin (no cheese) contain any hidden sugars?
While not overtly sweet, check the ingredient list for added sugars. Some processed ingredients may contain small amounts.
Can I customize the Egg McMuffin (no cheese) further to reduce calories?
Yes, you could request a smaller English muffin or ask for less butter or oil during preparation.
How does the Egg McMuffin (no cheese) compare to a scrambled egg at home?
A homemade scrambled egg will likely be lower in sodium and fat, offering more control over ingredients and preparation methods.



